Femoflor ®
Femoflor ® is a modern PCR-based test and the only diagnostic method that allows complex evaluation of vaginal microbiome composition, diagnosis of dysbiosis and detection of sexually transmitted infections. It is a first that with just one test is possible to determine the microbial vaginal composition in relation to all microorganisms inhabiting the female vaginal tract. Femoflor ® is the only test showing the full picture of the vaginal bacterial composition, distinguishing the norm from the disease. Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a condition where certain bacteria predominate in the vagina. BV is associated with an imbalance of „good“ and „harmful“ bacteria, usually found in a woman's vagina. Bacterial vaginosis is the most common vaginal condition in women aged 15-44 years. Bacterial vaginosis is very often asymptomatic and can increase the risk of contracting sexually transmitted infections, as well as compromising intimate and reproductive health. Pregnant women are at increased risk of developing BV. Bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy is associated with a risk of miscarriage, premature birth, low birth weight and infection of the newborn. Treatment is especially important for pregnant women.
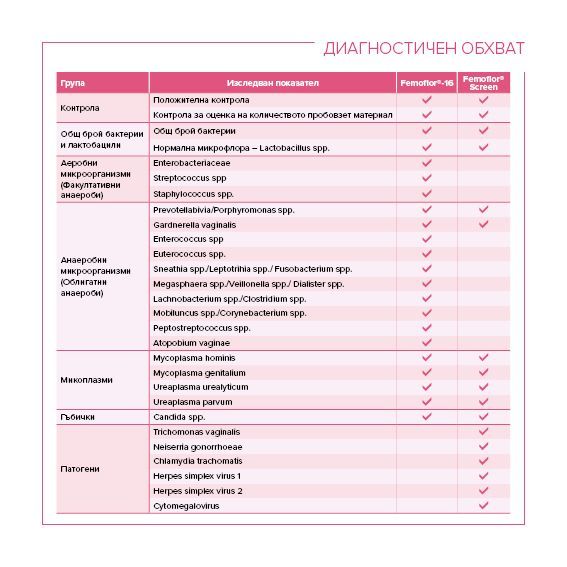
Diagnostic range: Lactobacillus spp., Enterobacterium spp., Streptococcus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Gardnerella vaginalis, Prevotella bivia, Porphyromonas spp, Eubacterium spp, Sneathia spp., Leptotrichia spp., Megasphaera spp., Veillonella spp., Dialister spp., Lachnobacterium spp., Mobiluncus spp., Corynebacterium spp., Clostridium spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Atopobium vaginae, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Ureaplasma parvum, Mycoplasma hominis, Candida spp. , Mycoplasma genitalium, Fusobacterium spp
Diagnostic Method: Real-time PCR assay
Research Material: Vaginal swab
Results within: 1 business day
Fee: BGN 125
Clinical application
Diseases associated with bacterial vaginosis
Download Our Brochure
NIFTY Pro®
The test includes non-invasive prenatal screening identifying the most common chromosomal aneuploidies and 84 microdeletion syndromes in maternal blood fetal DNA.
Diagnostic Range: In monoterminal pregnancy: Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome), monosomy X (Turner syndrome), XXX (Klinefelter syndrome), XXX and XYY, 84 microdeletion syndromes associated with deletions / duplications throughout the genome. In twin pregnancies, the test is only for Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) and the presence of the Y chromosome.
Diagnostic Method: NGS
Research Material: Venous blood from the pregnant woman (after 11 g.w.) in a special tube (6-10ml)
Results within: 10 business days
Fee: BGN 1300
Clinical application
The most common congenital genetic abnormalities
Download Our Brochure
Download Our Brochure
Femoflor Plus®
Femoflor plus® is a modern PCR-based test and the only diagnostic method that allows complex evaluation of vaginal microbiome composition, diagnosis of dysbiosis and detection of sexually transmitted infections. It is a first that with just one test is possible to determine the microbial vaginal composition in relation to all microorganisms inhabiting the female vaginal tract. Femoflor ® is the only test showing the full picture of the vaginal bacterial composition, distinguishing the norm from the disease.
Diagnostic Range: Lactobacillus spp., Enterobacterium spp., Streptococcus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Gardnerella vaginalis, Prevotella bivia, Porphyromonas spp, Eubacterium spp, Sneathia spp., Leptotrichia spp., Megasphaera spp., Veillonella spp., Dialister spp., Lachnobacterium spp., Mobiluncus spp., Corynebacterium spp., Clostridium spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Atopobium vaginae, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Ureaplasma parvum, Mycoplasma hominis, Candida spp. , Mycoplasma genitalium, Fusobacterium spp, Chlamydia trachomatis, Trichomonas vaginalis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Diagnostic Method: Real-time PCR assay
Research Material: Vaginal and cervical specimen
Results within: 1 business day
Fee: BGN 187
Diseases associated with the range of Femoflor plus®
Vaginitis; Cervicitis; Predisposition to sexually transmitted infections; Pelvic inflammatory disease; Infertility; Spontaneous abortions; Premature birth; Neonatal infection
Download Our Brochure
Download Our Brochure
NIFTY Pro® + NIFTY Mono®
In cell-free fetal DNA in maternal blood this test detects the presence of Trisomy 21 (Down's Syndrome), Trisomy 18 (Edwards Syndrome), Trisomy 13 (Patau's Syndrome), Monosomy X (Turner's Syndrome), XXX (Klinefelter's syndrome), XXX and XYY, 84 microdeletion syndromes associated with deletions / duplications throughout the genome, 27 severe dominant monogenic disorders resulting from de novo mutations in 18 genes.
In twin pregnancies, the test is only for Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) and the presence of the Y chromosome.
Diagnostic Range: Chromosomes 21, 18, 13, X, Y and the most common mutations in 18 genes
Diagnostic Method: NGS
Research Material: Venous blood from the pregnant woman (after 11 g.w.) in a special tube (6-10ml)
Results within: 10 business days
Fee: BGN 2600
Clinical application
The most common congenital genetic abnormalities
Download Our Brochure
Download Our Brochure
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common STD that can infect both men and women. It can cause serious, permanent damage to a woman's reproductive system. This can make it difficult or impossible for her to get pregnant later on. Currently, PCR assay is the gold standard for the diagnosis of chlamydial infections (See the diagnostic recommendations of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention HERE).
Diagnostic Range: Chlamydia trachomatis
Diagnostic Method: PCR Assay
Research Material: Cervical sample / Endometrial menstrual tissue / Urine / Ejaculate /
Results within: 1 business day
Fee: BGN 35
Diseases associated with chlamydial infection
Cervicitis; Urethritis; Epididymitis; Prostatitis; Premature birth; Pelvic inflammatory disease; Ectopic pregnancy, Infertility; Spontaneous abortions; Newborn infections
Download Our Certificate
Congenital Thrombophilia
This test analyzes genetic factors related to disorders of the coagulation system and the risk of increased blood clotting, as well as the risk of hypofibrinolysis.
Indications for the test are one or more miscarriages in the family, stillbirth, fetal growth retardation, preeclampsia, preparation for an in vitro procedure, use of hormonal contraceptives, varicose veins, cardiovascular disease in the family.
Number of Markers Tested:: 16
Polymorphisms Included: : Blood coagulation factors: FVL (R506Q), FII 20210G> A, FVII p.R353Q, FXIII p.V34L, FGB c.455G> A Fibrinolysis: PAI 4G / 5G, GPIIIa c.155T> C, TAFI c.505A> G Folate cycle: MTHFR c.77C> T, c.1298A> C, MTRR c.6A> G Other factors: ANXA5, VEGFA c.936C> T, c.-1154G> A, PP13, ACE (I / D)
Research Material: Venous or capillary blood with K2EDTA (purple tube)
Results within: 5-10 business days
Fee: BGN 40 - BGN 330, depending on the prescribed combination of polymorphisms
Diseases and Conditions
Family history of miscarriage ; Stillbirth; Fetal growth retardation; Preeclampsia; Preparation for in vitro procedure; Use of hormonal contraceptives; Varicose veins; Family history of cardiovascular diseases
Download Our Brochure
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by infection with the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. It can infect both men and women and is transmitted through vaginal, anal and oral sexual contact with an infected partner.
Gonorrhea is a very common infectious disease especially among young people aged 15-24. It can affect the genitals, rectum, and throat, depending on sexual practices.
Untreated gonorrhea can cause serious and permanent health problems in both women and men. The infection can also be spread perinatally from mother to baby during childbirth.
Currently, PCR analysis is the gold standard for the diagnosis of gonococcal infections (See the diagnostic recommendations of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention HERE).
Diagnostic Range: Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Diagnostic Method: PCR Assay
Research Material: Cervical sample / Endometrial menstrual tissue / Urine / Ejaculate /
Results within: 1 business day
Fee: BGN 35
Diseases associated with gonorrhea
Cervicitis; Urethritis; Epididymitis; Prostatitis; Premature birth; Pelvic inflammatory disease; Ectopic pregnancy, Infertility; Spontaneous abortions; Newborn infections
Download Our Certificate
Aneuploidies - Invasive Test
This test is prescribed when positive results from NIFTY Pro® and / or fetal morphology are registered. It is used for final conclusion regarding Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, monosomy X, syndrome XXX, triplodia.
This test for chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus involves taking chorionic villus sampling or performing amniocentesis. Both procedures involve the use of a fine needle to sample the amniotic fluid that surrounds the baby (amniocentesis) or to sample a placental cells (CVS).
These tests give a definite "Yes" or "No" result as to whether the fetus carries the suspected genetic mutation.
Although these invasive procedures provide a definitive diagnosis, they actually carry a minimal risk of miscarriage. Therefore, it is recommended to use non-invasive diagnostics as the primary source of research. The likelihood of miscarriage is often a dilemma for parents, and many women choose to have a NIFTY Pro® test before undertaking an invasive procedure.
Diagnostic Range: Chromosomes 21, 18, 13, X, Y
Diagnostic Method: Fragment analysis
Research Material: CVS, amniotic cells, blood, tissue
Results within: 5 business days
Fee: BGN 200
Clinical application
When positive results from NIFTY Pro® and / or fetal morphology are registered
ChromoSeq ®
ChromoSeq ® detects pathological copy number variations across the whole genome, including :
- Whole and partial chromosomal aneuploidies
- Unbalanced translocations
- Microdeletions and microduplications
- Deletions and duplications within single genes
Diagnostic Range: Pathological Copy Number Variations
Diagnostic Method: NGS
Research Material: Venous blood in K2EDTA, DNA, CVS, amniotic cells, abortive material
Results within: 20 business days
Fee: BGN 1,400
Aneuploidies - Abortive Material
This test analyses the most common chromosomal aneuploidies associated with loss of pregnancy. Abortive material analysis for the most common chromosomal abnormalities detects Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, monosomy X, syndrome XXX, triplodia, trisomy 9, trisomy 14, trisomy 15, trisomy 16, trisomy 22.
Diagnostic Range: Main panel: Chromosomes 21, 18, 13, X, Y; Additional panel: Chromosomes 9, 14, 15, 16 and 22
Diagnostic Method: Fragment analysis
Research Material: Abortive material in saline (not in formalin)
Results within: 5 business days
Fee: Main panel: BGN 200; Additional panel: BGN 220
Clinical application
Abortion
WES®
WES® detects pathological genetic variants in the whole protein coding sequence in the human genome.
Diagnostic Range: Approximately 20,000 genes
Diagnostic Method: NGS
Research Material: Venous blood in K2EDTA, DNA, CVS, amniotic cells, abortion material, tumor tissue
Results within: 3 months
Fee: BGN 3,800
Clinical application
Pathological genetic conditions
Group B Streptococcus (GBS)
Group B Streptococcus (group B strep, GBS) are bacteria that come and go naturally in the body. Most of the time the bacteria are not harmful for adults, but they can cause severe infection in newborns. Pregnant women can pass the bacteria to their babies during delivery.
The World Health Organization and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend for all pregnant women to get tested for GBS bacteria. Pregnant women should get tested when they are 36 through 37 weeks pregnant. The fastest and most reliable GBS test is designed specifically for the purposes of GBS screening PCR test. The test is quick and does not hurt.
Women who test positive for GBS are not sick. However, they are at increased risk for passing the bacteria to their babies during birth.
GBS bacteria can cause:
- Bacteremia (bloodstream infection) and sepsis (the body’s extreme response to an infection)
- Bone and joint infections
- Meningitis (infection of the tissue covering the brain and spinal cord)
- Pneumonia (lung infection)
- Skin and soft-tissue infections
Diagnostic Range: Streptococcus agalactiae
Diagnostic Method: PCR Assay
Research Material: Vaginal + Rectal swab
Results within: 1 business day
Fee: BGN 35
Clinical application
Group B strep test during the third trimester; Prevention of neonatal diseases associated with GBS infection
Download Our Brochure
Download Our Brochure
Immunity Package
A normal pregnancy is a state of tolerance between the mother's immune system and the half-foreign genetic material of the fetus inherited from the father. This tolerance is ensured by two main mechanisms:
- Soluble HLA-G protein secretion (part of the MHC class I HLA system), which functions in the trophoblasts - the contact zone between the fetus and the mother. In a normal pregnancy, HLA-G is released in high concentration and thus successfully suppresses the rejection of the fetus by the mother's immune system. At low concentration of HLA-G, the risk of miscarriage and preeclampsia increases greatly.
- Regulatory T cells of the immune system that suppress the secretion of Th1 cells (pro-inflammatory cytokines-interleukins 1, Tumor Necrotizing Factor) and stimulate the secretion of Th2 (anti-inflammatory cytokines). Increased Th1 secretion often leads to pregnancy complications, preeclampsia, premature birth, and low birth weight.
Diagnostic Range: Genetic variants in the genes HLA-G, IL1A, IL1B, TNFα are tested
Diagnostic Method: Sanger sequencing/ RFLP
Research Material: 6 ml venous blood / 2 ml peripheral blood
Results within: 10 business days
Fee: BGN 140
Clinical application
Pregnancy; Preeclampsia; T-cell immune response
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes, like type 2 diabetes, is characterized by insulin resistance and an inability to properly metabolize glucose and elevated blood sugar levels. It develops during pregnancy and usually disappears after it, but 20-50% of affected women have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later after delivery. Mother with gestational diabetes and fetus are at risk during pregnancy and after birth. The development of gestational diabetes in the mother and its untimely management can lead to macrosomia, respiratory problems, and jaundice in the newborn, as well as severe hypoglycemia immediately after birth. Early diagnosis of predisposition to gestational diabetes would assist obstetricians in monitoring pregnancy, choosing an appropriate diet, exercise for the expectant mother and drug therapy, if necessary.
At increased risk of developing gestational diabetes are women:
- who are overweight (Вody mass index about 30)
- over 30-35 years
- with sugar in the urine
- with high blood pressure or other medical complications
- with previous birth of an overweight child
- with gestational diabetes in previous pregnancies
- with family history of diabetes
- with type 1 or type 2 diabetes before pregnancy
Diagnostic Range: TCF7L2; FTO; GCK; MBL2
Diagnostic Method: Sanger sequencing
Research Material: 3-6 ml venous blood / 2 ml peripheral blood
Results within: 10 business days
Fee: BGN 200
Clinical application
Gestational diabetes; Type 2 diabetes; Genetic predisposition; Nutrition, Healthy Eating
Folate
Folate (Vitamin B9) is part of the B vitamins group and is associated with the normal development of the fetus during pregnancy, the formation of red blood cells, proper DNA synthesis, methylation, and detoxification of the cell.
The Folate genetic test involves the analysis of genetic variants in the MTHFR gene associated with the proper absorption of folic acid and a possible risk of vitamin deficiency, which is often accompanied by an increase in homocysteine levels. The test is used to determine the need for additional folic acid intake in order to improve the quality of life in people of different ages.
Diagnostic Range: Absorption of folic acid
Diagnostic Method: RFLP
Research Material: 3-6 ml venous blood / 2 ml peripheral blood
Results within: 10 business days
Fee: BGN 80
Clinical application
Folic acid deficiency



_600x600.jpg?alt=media)